Barrett’s Esophagus
Cellvizio® is the real-time in vivo cellular imaging platform that is an adjunct to the standard of care and enables physicians to detect and monitor the progression of GERD to Barrett’s Esophagus (BE) over time using proprietary advanced imaging technology.
Esophageal cancer is the fastest growing cancer²…
…where

4 out of 5 patient die within 5 years of their diagnosis3
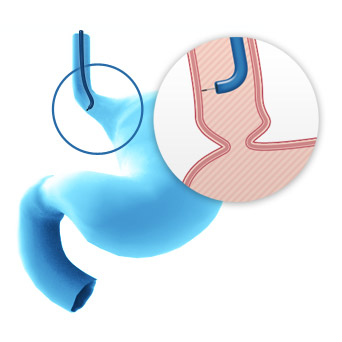
Based on the growing prevalence of BE and EAC among patients, it is obvious that inadequate surveillance of the esophagus with standard biopsy techniques leads to missed diagnoses of dysplasia and EAC altogether, casting doubt on the role of surveillance endoscopy as it is today.5
The Seattle Protocol, or gold standard for index endoscopy procedures, calls for 4-quadrant biopsies every 1 to 2 centimeters. Even if adhered to, the Seattle Protocol
proves to have lower detection rates of dysplasia due to the irregularity and complexity of esophageal tissue, suggesting that this systematic approach alone to identifying random islands of dysplasia is insufficient.5
With Cellvizio® as an adjunct to Seattle protocol, physicians have clear, minimally invasive visualization of the esophagus at the cellular level to obtain a comprehensive assessment of the extent of disease and make real-time therapeutic decisions.
Cellvizio® Clinical Value
Cellvizio® is powered by a technology known as probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy, or pCLE, which allows for visibility of cell architecture at the microscopic level. Compared to the standard, random biopsy protocol alone, the addition of Cellvizio® as an adjunct technology doubles the detection rate of Barrett’s Esophagus6, where 1.7 times more lesions were detected with Cellvizio® and WLE when compared to WLE and NBI alone7,8. When compared to WLE random biopsies, Cellvizio® provides a significantly higher diagnostic yield and accuracy with reduced sampling error.5,7
Cellvizio® advanced imaging and its easy integration into existing workflows allows physicians to better target biopsies within focused areas of concern, augmenting conventional technologies and techniques, and improving the ability to detect and monitor cellular changes.
9
studies
688
patients

1,299
lesions
Compared to random biopsies, the increases in the per patient pooled detection rate of neoplasia with pCLE were as follows:

assessed the benefits of pCLE as an adjunct to random 4-quadrant biopsies in the surveillance of patients with BE for dysplasia and early EAC detection:

For surgeons, this technology has the potential to reduce inappropriate endoluminal therapy for non-neoplastic conditions, thus improving overall procedure-related complications, optimizing surveillance intervals, and limiting histological analysis of insignificant lesions.12 This helps improve diagnostic yield and increase the detection of dysplastic lesions from 34% to 68%.7
GERD/Barrett’s Esophagus Monitoring
GERD/Barrett’s Esophagus Monitoring
Cellvizio® makes it possible for us to: rule-in or rule-out the presence of pre-cancerous cells (…) perform improved surgical intervention (…) monitor for the presence of cancerous cells after the procedure.
Dr. J. Burnette, Piedmont Macon North Hospital
Cellvizio® makes it possible for us to: rule-in or rule-out the presence of pre-cancerous cells (…) perform improved surgical intervention (…) monitor for the presence of cancerous cells after the procedure.
Cellvizio® is part of routine clinical practice
See how Dr. Joseph Burnette, a general surgeon with special interest in reflux uses Cellvizio® on all his chronic reflux patients.

Cellvizio® adds 3-5 minutes, while more than doubling detection of Barrett’s Esophagus vs. conventional biopsies.
Dr. A. McNair Jr.
New Gulf Coast Surgery Center
Patient Management

Cellvizio® leads to better informed patient management by providing additional advanced imaging, enabling real-time tissue assessment and early detection. Physicians are able to rule-in or rule-out intestinal metaplasia in the presence of GERD symptoms9, allowing for earlier detection of BE6 and the monitoring of such disease.7,8
Physicians also are able to define the location and lateral extent of neoplasia inducing clinical intervention10, as well as differentiate lesions that are not amenable to EMR and determine the margins of a lesion before endoscopic resection12. Therefore, pCLE can lead to positive redirection of therapy.11
Economic Benefit
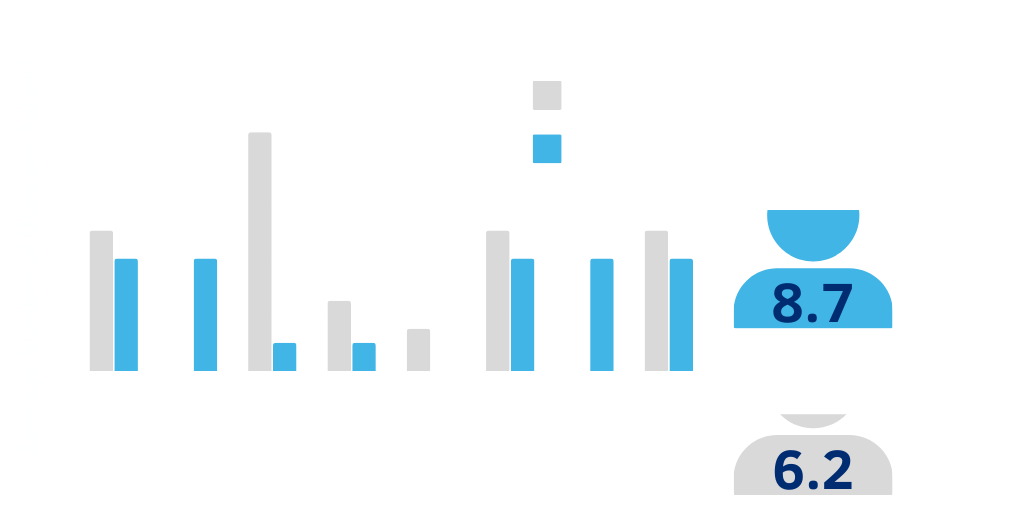
According to data presented at DDW 2023, “the use of Cellvizio® is associated with lower health services utilization of endoscopy, anesthesia, biopsy, ablation and higher patient satisfaction.”13
Cellvizio® enables physicians to assess areas of concern and target biopsies for increased diagnostic yield, optimizing utilization of health service resources and reducing overall number of unnecessary endoscopy procedures required for diagnosis and treatment.13
Tissue characterization using Cellvizio® Gastroflex UHD miniprobe
Tissue characterization
using Cellvizio® Gastroflex
UHD miniprobe
Squamous Epithelium
Criteria: squamous epithelium with flat and scale-like cells, intrapapillary loops
Intestinal Metaplasia
Criteria: regular columnar-lined epithelium, dark mucin in goblet cells easily identified, equidistant and regular cells, glands equal in size and shape
Adenocarcinoma
Criteria: epithelial surface appearing saw-toothed, non equidistant glands, glands unequal in size and shape, pleomorphic and enlarged cells
References & disclaimers
- Bhardwaj A. et al. Barrett’s Esophagus: Emerging Knowledge and Management Strategies. Pathology Research International, 2012. doi: 10.1155/2012/814146.
- Chai J. et al. Esophageal malignancy: A growing concern, World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6521.
- Desai M. et al. Prevalence of HGD and adenocarcinoma on index endoscopy in BE, Gastrointest Endosc, 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2018.09.041.
- Visrodia K. et al. Magnitude of Missed Esophageal Adenocarcinoma After Barrett’s Esophagus Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology, 2016. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.11.040.
- DeMeester S. et al. High definition probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy review and meta-analysis for neoplasia detection in Barrett’s esophagus. Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2022. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2022.06.001.
- Richardson C. et al. Real-time diagnosis of Barrett’s Esophagus: a prospective, multicenter study comparing confocal laser endomicroscopy with conventional histology for the identification of intestinal metaplasia in new users, Surgical Endoscopy, 2018. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6420-9.
- Sharma P. et al. Real-time increased detection of Neoplastic tissue in Barrett’s Esophagus with pCLE; Final results of a multi-center prospective international randomized controlled trial, Gastrointest Endosc, 2011. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.04.004.
- Canto M. et al. In vivo endomicroscopy improves detection of Barrett’s Esophagus related neoplasia: a multicenter international randomized controlled trial, GIE, 2013. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.09.020.
- Kiesslich R. et al. In vivo histology of Barrett’s Esophagus and Associated Neoplasia by CLE, Clinical Gastro and Hepatology, 2006.
- Wang K. et al. Use of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) in gastrointestinal applications. A consensus report based on clinical evidence. UEGW Journal, 2015. doi: 10.1177/2050640614566066.
- Caillol et al. Probe confocal laser endomicroscopy in the therapeutic endoscopic management of Barrett’s dysplasia. Annals of Gastroenterology, 2017. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0138.
- Al-Mansour. et al. SAGES TAVAC safety and efficacy analysis confocal laser endomicroscopy. Surg Endosc, 2020. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07607-3.
- Randhawa N, et al. A comparison of patient satisfaction and healthcare resource use in patients with Barrett’s Esophagus using CLE based approach versus standard of care. DDW 2023 Poster. https://eposters.ddw.org/ddw/2023/ddw-2023/377845/navkiran.randhawa.a.comparison.of.patient.satisfaction.and.healthcare.resource.html
Cellvizio® I.V.E. with Confocal Miniprobes™ are regulated Medical Devices, CE marked (CE 0459) (Class IIa – NB : G-MED) and FDA cleared. Cellvizio® is a registered trademark and Confocal Miniprobe™ is a trademark of Mauna Kea Technologies. Cellvizio® I.V.E. with Confocal Miniprobes™ is a confocal laser system with fiber optic probes that is intended to allow imaging of the internal microstructure of tissues including, but not limited to, the identification of cells and vessels and their organization or architecture. Once connected to the Cellvizio® I.V.E.: The GastroFlex™ UHD and ColoFlex™ UHD Confocal Miniprobes™ are intended to allow imaging of anatomical tracts, i.e., gastrointestinal systems, accessed by an endoscope or endoscopic accessories. Please consult labels and instructions for use. These statements and the associated reference to specific clinical studies, are not intended to represent claims of safety or effectiveness for detecting or treating any specific condition or disease state. Rather this information is intended to provide useful reference to selected published literature describing physician experiences with the associated clinical uses. Any diagnostic assessment should always be made by the attending physician, based on the evaluation of all sources of clinical, endoscopic and other relevant information. These statements have not been reviewed, cleared, or approved by the U.S. FDA. The use of this medical device is exclusively reserved for health professionals. Product availability cannot be guaranteed in all countries. For further information, please contact your local sales representative.
News
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE TO READ

Mauna Kea Technologies Announces New Commercial Organization to Accelerate Growth Outside the United States

Mauna Kea Technologies announces Initiation of Coverage by Allinvest Securities

Mauna Kea Technologies announces its 2026 financial calendar highlighted by its participation in several investor forums
Find out more by downloading the
Cellvizio Brochure